In the last blog post, we discussed about a brief introduction to network topologies and focused particularly on the ">star topology. In this blog post we will discuss about the features, pros and cons and the usage of bus topology.
Bus topology -
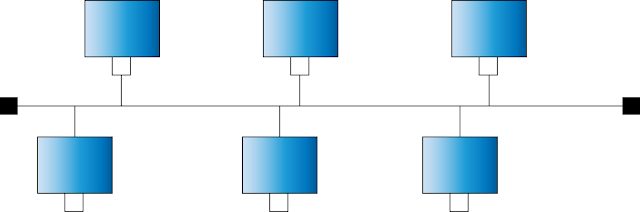
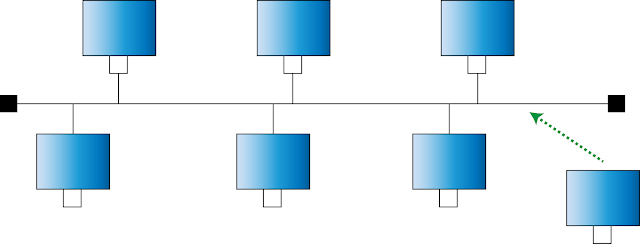
In a bus topology, all the devices are connected to a central cable (called the bus), through interface connectors (BNC connectors), as shown below:
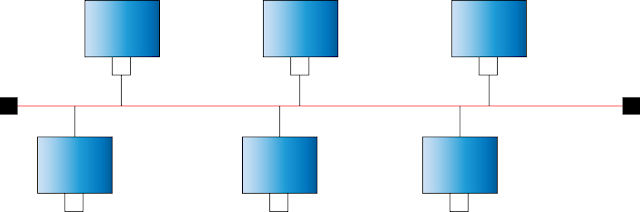
In a bus topology, terminators are added, as shown by the red squares in the above figure at the ends, to prevent reflection of signals. In a bus topology, only one device may communicate at a time. To avoid collision of packets, all other devices should wait until the bus line is free for them to communicate. A protocol called Distribute Access Protocol (DAP) is used to determine which device can communicate at any instance.
Due to the centralized use of the bus line and since the bus line is an Ethernet cable, the IEEE standards limit the number of devices that could be connected to it. Therefore, there is a limited number of network devices that could be connected to a bus network.
This architecture leads to various advantages and disadvantages of using bus networks.
The network could easily add a new device just by intercepting the bus cable
2. Less cable length and less networking devices make the bus network a very economical option -
Less cable length is required to connect to the bus line. Also, there is no necessity of switches or hubs as in star networks. Therefore, bus networks are a very economical option when choosing networks.
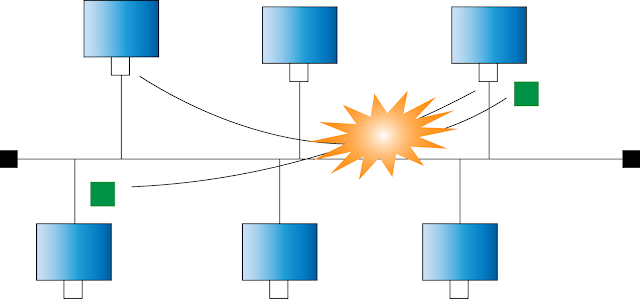
If the bus cable malfunctions, none of the devices will be able to communicate.
4. Difficulty in troubleshooting
It is difficult to troubleshoot at times when a single node should be evaluated. Needs additional devices for evaluation and takes time. So, the difficulty in troubleshooting a bus network is one of the major drawbacks.
5. No intelligence in the network.
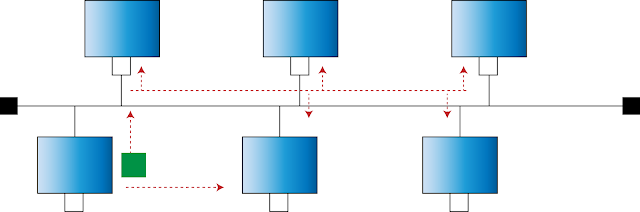
When a device needs to communicate with another device, packets are broadcasted to all the devices available in the network. Also, to prevent collision of packets, all other devices should wait until this identification of the correct device and communication takes place. Therefore, this is not an efficient and intelligent approach of communication between devices.
7. Number of devices vs Bandwidth per device
Since all the devices share the bus line, the greater the number of devices, the lesser the bandwidth per device.
In this blog post-
In a bus topology, all the devices are connected to a central cable (called the bus), through interface connectors (BNC connectors), as shown below:
More topologies to discover:
In a bus topology, terminators are added, as shown by the red squares in the above figure at the ends, to prevent reflection of signals. In a bus topology, only one device may communicate at a time. To avoid collision of packets, all other devices should wait until the bus line is free for them to communicate. A protocol called Distribute Access Protocol (DAP) is used to determine which device can communicate at any instance.
Due to the centralized use of the bus line and since the bus line is an Ethernet cable, the IEEE standards limit the number of devices that could be connected to it. Therefore, there is a limited number of network devices that could be connected to a bus network.
This architecture leads to various advantages and disadvantages of using bus networks.
Advantages of using bus topologies -
1. Setting up the network and upgrading is easy -The network could easily add a new device just by intercepting the bus cable
Less cable length is required to connect to the bus line. Also, there is no necessity of switches or hubs as in star networks. Therefore, bus networks are a very economical option when choosing networks.
3. Ease of troubleshooting -
If a device needs to be removed, then it could be removed easily without disturbing the communication between other devices.
Disadvantages of using bus topologies -
1. If the central cable (the bus cable) malfunctions, then the whole network shuts down -If the bus cable malfunctions, none of the devices will be able to communicate.
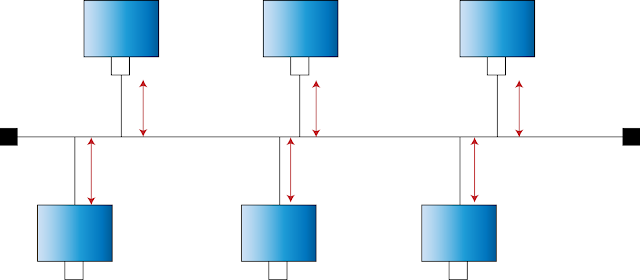
2. Collision of packets -
When packets are sent from one node to another node, collision of packets could occur if they have to travel in the same path at the same time. Such collisions could be detected using CSMA/CD.
3. Limitations on the cable length and the number of devices that could be connected -
There is a limit for the number of devices that could be connected. Additional devices cannot be connected unless replaced by an existing device's connection.
4. Difficulty in troubleshooting
It is difficult to troubleshoot at times when a single node should be evaluated. Needs additional devices for evaluation and takes time. So, the difficulty in troubleshooting a bus network is one of the major drawbacks.
5. No intelligence in the network.
When a device needs to communicate with another device, packets are broadcasted to all the devices available in the network. Also, to prevent collision of packets, all other devices should wait until this identification of the correct device and communication takes place. Therefore, this is not an efficient and intelligent approach of communication between devices.
6. Less privacy
Less privacy in the network as packets are send to all the devices before one device captures when the addresses match.
7. Number of devices vs Bandwidth per device
Since all the devices share the bus line, the greater the number of devices, the lesser the bandwidth per device.






This is a brilliant blog! I'm very happy with the comments!.. Bus Running Times
ReplyDeleteNo doubt this is an excellent post I got a lot of knowledge after reading good luck. Theme of blog is excellent there is almost everything to read, Brilliant post. freight quote
ReplyDeleteCool stuff you have got and you keep update all of us. furniture shipping near me
ReplyDelete