In the last blog posts we discussed about the star topology and bus topology. This is the third of the series of blog posts on network topologies. This blog post will explain about the mesh/fully connected topology, its pros and cons and the typical usage of its architecture.
Mesh or Fully connected topology -
In a mesh or fully connected topology all the nodes are interconnected with each other without the use of a common media.
For example, as we discussed, in a star topology, all the networking devices were interconnected using a switch or a hub and in the bus topology, all the devices were interconnected using a bus line.
However, in mesh or fully connected topology, as the name implies, all the devices are interconnected directly with each other. Due to this nature of connectivity, as shown below, it is the most expensive to build type of network architecture, as it requires the maximum number of connections as a whole.
Mesh or Fully connected topology -
In a mesh or fully connected topology all the nodes are interconnected with each other without the use of a common media.
For example, as we discussed, in a star topology, all the networking devices were interconnected using a switch or a hub and in the bus topology, all the devices were interconnected using a bus line.
More topologies to discover:
However, in mesh or fully connected topology, as the name implies, all the devices are interconnected directly with each other. Due to this nature of connectivity, as shown below, it is the most expensive to build type of network architecture, as it requires the maximum number of connections as a whole.
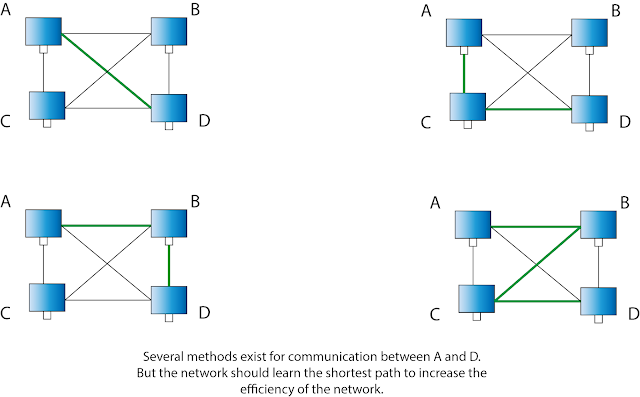
In a mesh topology, the system should calculate the number of links or also called "hops" it should take in order to reach the node. Consider the following diagram in which computer A wants to communicate with computer D :
Now you may think why we should even concern the alternative pathways when there is a direct link between any two computers. This is specially needed if the direct link between any two computers is broken.
This way of choosing alternative pathways to communicate with devices, when another link is broken in a network, is called self healing technology.
Advantages of mesh or fully connected topology -
1. Reliability (ensuring easy troubleshooting) of the network.
Even when a link is broken, there are many possibilities that the network can choose to ensure the reliability and efficiency of communication as shown below :
2. Privacy -
As described above, mesh topologies are primarily used for radio frequency transmission networks like wireless technology and mobile to mobile communication over short distances. These wireless technologies are the most susceptible networks for attacks as penetration to such networks is easy as hardware equipments are seldom needed to join the existing network. Therefore, privacy is highly ensured in mesh networks due to the nature of one : one connection between the devices.
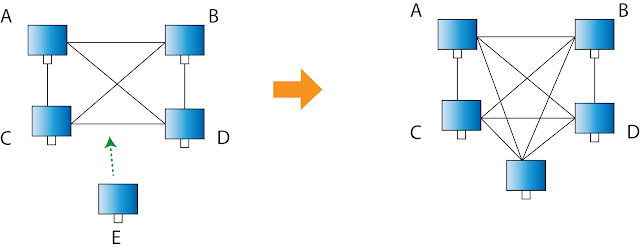
3. Expansion of the network is easy.
For example, if another computer called F wants to join the network, the upgrade could be done even when all the nodes are communicating with each other due to the fully connected nature of the topology :
Disadvantages of mesh or fully connected topology -
1. Complexity -
As you saw in the above explanation on the expansion of the network, when each node or device is added, many links have to be created to maintain the fully connected network property. In fact, if there are n nodes, then there should be n*(n - 1)/2 connections. Therefore, as new connections are made the complexity for maintenance and troubleshooting increases rapidly.
2. Expensive -
As stated earlier, fully connected networks are the most expensive to build as there are as many connections compared to other network topologies.
3. Redundant links -
More often many links are seldom or not at all used and are a waste of implementing. However, we may not remove these links as if one link fails these links may be needed to operate as alternate pathways.
Usage -
As you could see, mesh topology has the highest number of links as a network. Therefore, this network is very expensive to build. However, this network gives the best safety when privacy of communication is concerned. Therefore, mesh topology is generally used for wireless networks, where privacy or data security is of utmost importance as data sniffing could be easily carried out in wireless networks.






Comments
Post a Comment