What is a network access point?
Network access points are places which provide access to national and global networking traffic.
Remember that network access point was an access method that was widely used before they were replaced by Internet Exchange Points (IXP s).
Why need network access points?
Think that you want to send some data to a friend who is living about 500km away from you. How would you send the data to your friend. How can you connect to the friend and vice versa?
The most common method to do this is to connect to your ISP (Internet Service Provider) and send the data and on the receiving end the friend can receive the data from the same ISP or from a different ISP.
If you are on one network and the friend is on another network (two different ISP s) how can you connect?
That is where you need network access points. Network access points, as mentioned earlier in this blog post, are places which provide access to national and global networking traffic.
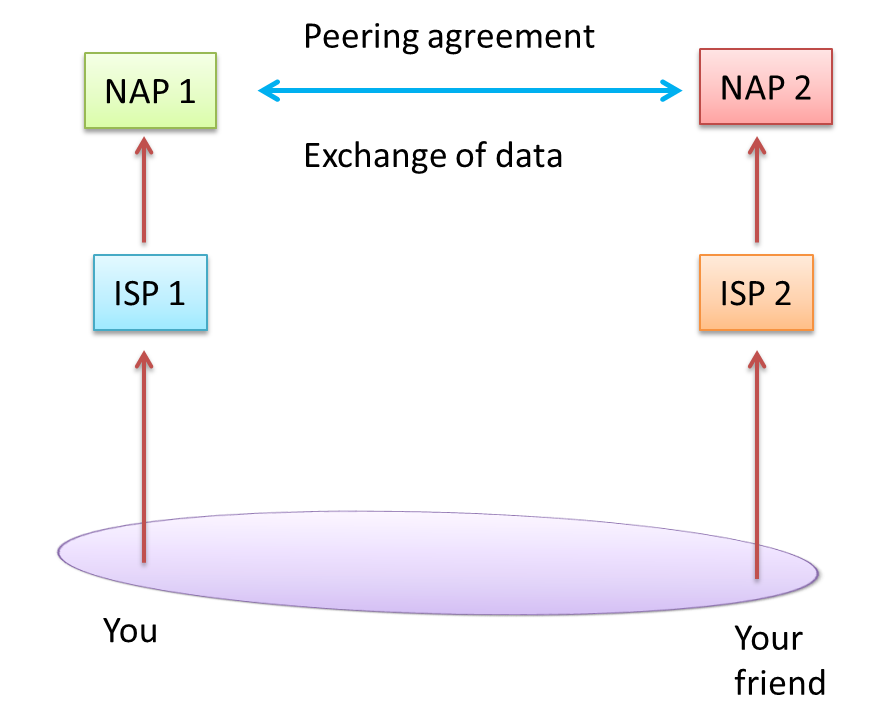
Consider the following diagram.
As shown your ISP may connect to NAP 1 and your friend's ISP may connect to NAP 2. Companies connecting to NAP s should enter into peering agreements in order to exchange information.
Now the two ISP s can share data, which intern facilitates you and your friend to exchange data.
Note: There is no need to always connect to an ISP to send data. In some areas, some companies (which are not ISP s) could act as ISP s or some companies (which are not ISP s) could connect to ISP s. Either way long distance or short distance communication can be done using network access points.
Moreover, there is no need that the two above mentioned ISP s connect to two network access points. Peering agreements between the two ISP s could occur within the same network access point.
However, the real need of NAP s occur when you are connecting to global traffic. Suppose you want to connect to a website called www.abcde.com.
You can request data from the server at abcde and in turn the server sends information back to you. The whole transfer of information between you and the server takes place through network access points (NAP s).
In summary, network access points (NAP s) are places which provide access to national and global network traffic. Internal as well as worldwide communication may take place through these network access points.
Companies themselves could act as NAP s or they can connect to a single or multiple access point(s). To transfer data, companies should enter into peering agreements (similar to protocols). By entering into peering agreements and connecting via network access points, these companies could minimize fault tolerance and enhance efficiency when providing access to data transmissions for their users.
Network access points are places which provide access to national and global networking traffic.
Remember that network access point was an access method that was widely used before they were replaced by Internet Exchange Points (IXP s).
Why need network access points?
Think that you want to send some data to a friend who is living about 500km away from you. How would you send the data to your friend. How can you connect to the friend and vice versa?
The most common method to do this is to connect to your ISP (Internet Service Provider) and send the data and on the receiving end the friend can receive the data from the same ISP or from a different ISP.
If you are on one network and the friend is on another network (two different ISP s) how can you connect?
That is where you need network access points. Network access points, as mentioned earlier in this blog post, are places which provide access to national and global networking traffic.
Consider the following diagram.
As shown your ISP may connect to NAP 1 and your friend's ISP may connect to NAP 2. Companies connecting to NAP s should enter into peering agreements in order to exchange information.
Now the two ISP s can share data, which intern facilitates you and your friend to exchange data.
Note: There is no need to always connect to an ISP to send data. In some areas, some companies (which are not ISP s) could act as ISP s or some companies (which are not ISP s) could connect to ISP s. Either way long distance or short distance communication can be done using network access points.
Moreover, there is no need that the two above mentioned ISP s connect to two network access points. Peering agreements between the two ISP s could occur within the same network access point.
However, the real need of NAP s occur when you are connecting to global traffic. Suppose you want to connect to a website called www.abcde.com.
You can request data from the server at abcde and in turn the server sends information back to you. The whole transfer of information between you and the server takes place through network access points (NAP s).
In summary, network access points (NAP s) are places which provide access to national and global network traffic. Internal as well as worldwide communication may take place through these network access points.
Companies themselves could act as NAP s or they can connect to a single or multiple access point(s). To transfer data, companies should enter into peering agreements (similar to protocols). By entering into peering agreements and connecting via network access points, these companies could minimize fault tolerance and enhance efficiency when providing access to data transmissions for their users.








Comments
Post a Comment